Artificial Intelligence and blockchain already stand out as two of the most groundbreaking technologies this decade.
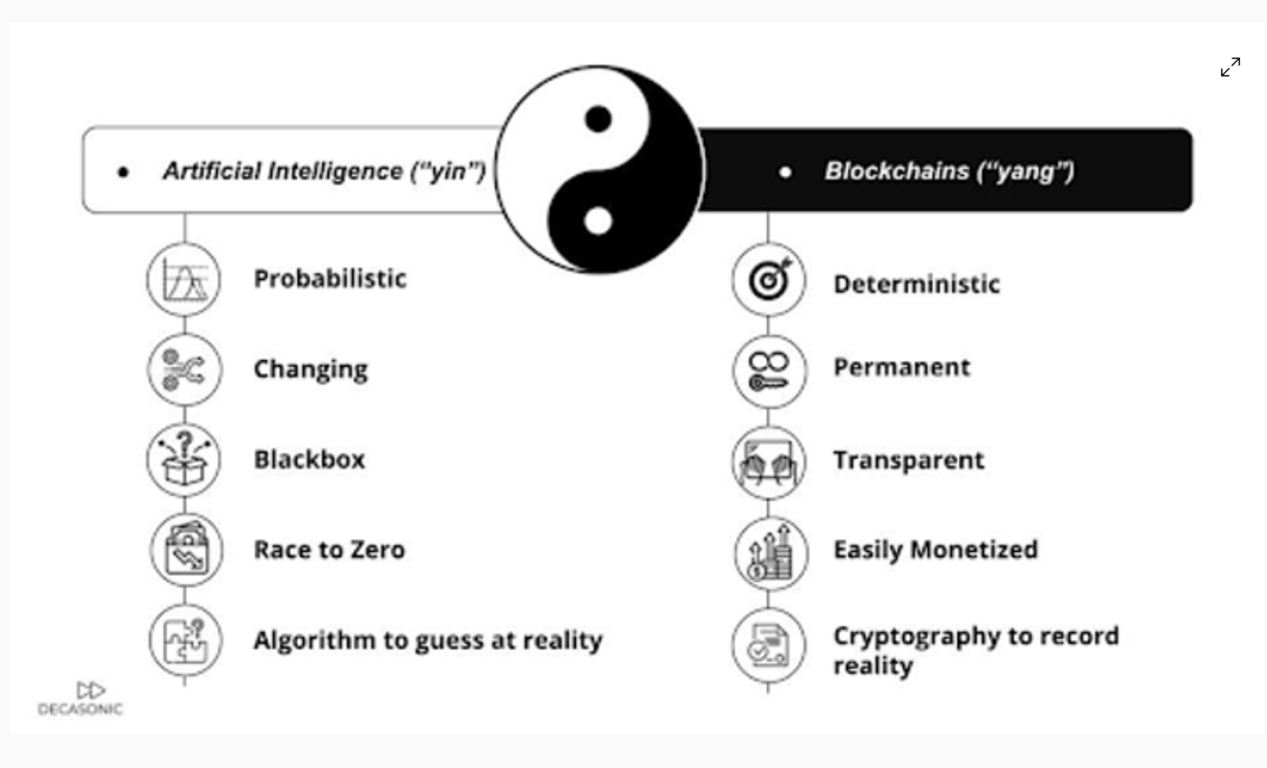
On the one hand, blockchain and Web 3.0 technologies ushered in a new deterministic, transparent, and trustless paradigm of decentralization secured by cryptography. On the other, AI boasts scalable creation, unparalleled automation, accurate data analysis, and more.
However, these unique technologies came with unique challenges. AI’s domain is marked by probability, centralization, and opaque processes while blockchain still faces scalability, interoperability, and user experience issues.
An innovative way to address these challenges was to merge AI’s data analysis with the security that blockchain technology provides. With each technology tackling or covering up for the challenges faced by the other, this led to the convergence of the two otherwise distinct technologies.
Foundational Layers of AI in Web3
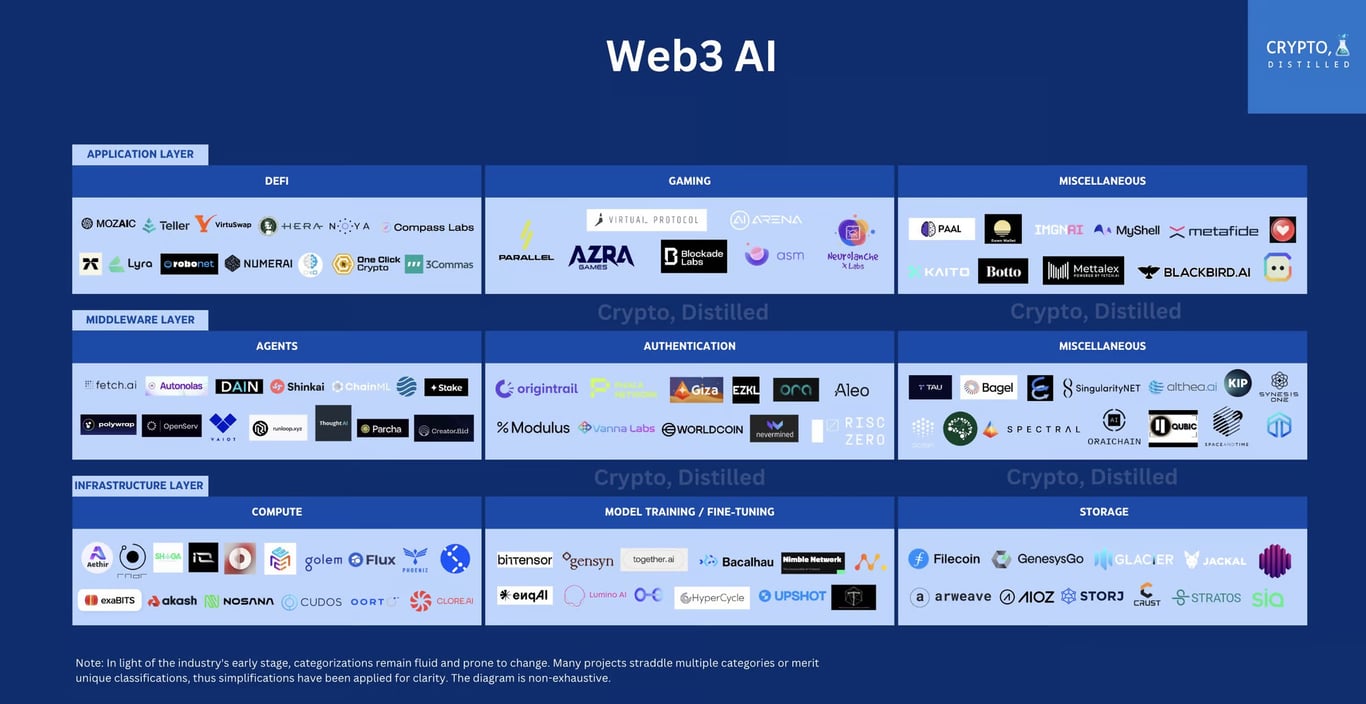
Web3’s AI tech stack describes how AI technologies fit within the broader Web3 ecosystem. This stack is made up of foundational layers that provide the necessary infrastructure for AI to function effectively in Web3.
Base/Infrastructure Layer
The base or infrastructure layer is the core of the stack. It encompasses blockchain protocols, cloud infrastructures, and networks essential for establishing rules, consensus mechanisms, and creating native assets.
At this foundational level, integrating AI into blockchain protocols and cloud infrastructures becomes imperative for the development of robust, scalable, and secure AI models. This stage requires leveraging cryptographic networks for immutable data storage, implementing smart contracts for decentralized AI model interactions, and harnessing cloud infrastructures for extensive computational resources.
Projects operating within this layer demand highly skilled teams proficient in both AI and crypto, capable of pioneering innovations that significantly improve data privacy, security, computational efficiency, and other critical aspects.
This base layer can be further split into:
- Computation Layer
- Network Layer
- Data Storage Layer
- Model Layer
Computation Layer
The computation layer in the stack leverages decentralized computing resources to power AI applications. This layer harnesses the capabilities of blockchain-based compute marketplaces, which serve as decentralized platforms to buy and sell computational resources. These peer-to-peer (P2P) marketplaces are crypto-incentivized to maintain secure decentralization. However, it's crucial to understand that the actual GPU processing takes place off-chain.
At this layer, AI algorithms and models can access computing power from a distributed network of nodes, eliminating the need for centralized infrastructure. This decentralized approach allows AI applications to fully optimize their products and offer new use cases, such as predictive analytics, machine learning, and natural language processing.
Data Storage Layer
The data storage layer leverages decentralized data markets to power AI applications. These decentralized data markets enable the exchange of data in a secure, transparent, and peer-to-peer manner, facilitating the seamless flow of information across the ecosystem.
At this layer, data privacy and user control are paramount considerations. Blockchain technology ensures the immutability and integrity of data stored within decentralized networks, while cryptographic techniques safeguard data privacy through encryption and secure access controls. Users retain ownership and control over their data, granting permissions for its use and monetization based on transparent and auditable smart contracts.
Decentralized data markets fuel AI by providing access to diverse and high-quality datasets, enhancing the robustness and accuracy of AI models. By tapping into decentralized data sources, AI applications can mitigate bias and improve generalization, leading to more reliable and ethical outcomes.
Network Layer
The network layer within the AI in Web3 tech stack is dedicated to enhancing connectivity and interoperability across the ecosystem. This layer encompasses both the infrastructure for network connectivity and mechanisms for improving communication across systems.
Focused on enhancing AI model accessibility, interoperability, and data exchange across various platforms and networks, this layer includes decentralized networks for AI computation, decentralized data-sharing solutions like IPFS, and interoperability mechanisms to connect different AI models and datasets.
Projects operating within this layer aim to achieve significant ecosystem improvements through decentralized AI, fostering a minimum viable ecosystem where AI and blockchain can interact seamlessly. This enhances overall system performance and user experience.
Examples of projects within this layer include Allora AI Commune AI,
Model Layer
The model layer encompasses AI models that operate on decentralized networks. One notable approach is federated learning, where AI models are trained across a network of decentralized devices or nodes without centralizing data. This decentralized training process preserves user privacy by keeping data localized and enables AI models to learn from diverse and distributed sources, enhancing their robustness and adaptability.
Another key aspect of the model layer is model sharing. Decentralized platforms allow AI developers to share and collaborate on pre-trained models. By leveraging these decentralized networks, developers can access a diverse range of models.
Decentralized model marketplaces enable the buying, selling, and licensing of AI models transparently and securely. These marketplaces utilize blockchain technology to ensure trust and transparency in model transactions while providing incentives for model creators.
Middleware/Interface/Service Layer
While the base layer facilitates unrestricted GPU access, middleware is necessary to link this computational resource to on-chain smart contracts in a trust-minimized manner for use by Web3 applications. The middleware/service/interface layer in the convergence of AI and Web3 acts as a crucial intermediary, facilitating seamless communication and data management between the underlying infrastructure layer and applications. This layer encompasses a range of tools, APIs, SDKs, and frameworks designed to streamline the development process and enhance the functionality of AI applications within the Web3 ecosystem.
At the service layer, the primary focus is on equipping developers with the necessary resources to efficiently build, deploy, and manage AI models. This includes frameworks for AI model development, tools for data preprocessing and augmentation, and services for model optimization and conversion.
Middleware solutions such as zero-knowledge proofs play a crucial role in connecting decentralized computing resources to on-chain smart contracts in a trust-minimized manner. ZKPs enable decentralized marketplaces for verifiers to validate inference outputs while preserving data and model parameters' privacy.
Besides zero-knowledge proofs, Web3 developers need tools, SDKs, and services to effectively construct applications (AI agents and AI-driven automated trading strategies for example). Many of these protocols also serve as application hubs that allow users to access completed applications developed on their platforms directly.
Examples of platforms within this layer include Numbers, Fetch.ai, DAIN, Chain ML, Origin Trail, EZKL, SingularityNet, Spectral Labs, Oraichain, Ocean, etc.
Application Layer
The application layer represents the most user-facing aspect of the tech stack, encompassing a diverse array of services and applications spanning finance, gaming, etc. Leveraging the infrastructure provided by the underlying layers, this layer hosts applications that integrate AI and blockchain to offer advanced services and functionalities. Categories within this layer include decentralized AI applications, AI-driven marketplaces, and platforms using AI for personalization, security, and automation.
While this layer remains in its infancy and relies on centralized infrastructure, early examples include smart contract auditing, blockchain-specific chatbots, metaverse gaming, image generation, and trading and risk-management platforms. As underlying infrastructure advances and zero-knowledge proofs (ZKPs) mature, next-gen AI applications will emerge, offering functionalities that are presently difficult to imagine.
Key Uses of AI in Web3
AI plays a pivotal role in various key use cases within Web3:
- Finance: In finance, AI-powered algorithms are utilized for tasks such as predictive analytics, risk assessment, fraud detection, and automated trading. AI models can analyze vast amounts of financial data to identify patterns and trends, enabling more informed investment decisions and risk management strategies. AI-powered DeFi platforms also utilize smart contracts and oracles to automate DeFi operations.
- Decentralized Autonomous Organizations: AI enhances the governance and decision-making processes of DAOs by providing predictive analytics, sentiment analysis, and consensus mechanisms. To do this, AI algorithms can analyze community feedback and voting patterns to inform decision-making and optimize resource allocation within DAOs.
- Security: AI strengthens security within Web3 ecosystems by detecting and mitigating cyber threats, identifying vulnerabilities, and enhancing data privacy. AI-powered cybersecurity solutions utilize machine learning algorithms to monitor network traffic, detect anomalous behavior, and respond to security incidents in real-time. AI-driven encryption techniques and decentralized identity management systems also enhance data security and user privacy in decentralized networks.
- User Experience: AI improves user experience in Web3 applications through personalization, recommendation systems, and natural language processing (NLP). AI does this by using algorithms to analyze user behavior and preferences to deliver tailored content, optimize user interfaces, and provide intelligent assistance. AI chatbots and virtual assistants have also been used to enhance user engagement and support in applications, enhancing overall user satisfaction and retention.
- Content Creation and Management: AI can automate content creation to generate personalized content, curate relevant information, and moderate user-generated content to ensure compliance with community guidelines and regulatory requirements.